Introduction
The nervous system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that transmit signals throughout the body, coordinating and controlling various bodily functions. When the nervous system becomes dysregulated, it can lead to a range of physical and mental health issues.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the concept of nervous system dysregulation, its causes, common signs, and its impact on gut health. We will explore techniques and supplements that can help reset and regulate the nervous system, promoting a healthier mind and body.
What is the Nervous System?

The nervous system is an intricate network that includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves spread throughout the body. It plays a crucial role in transmitting signals between different parts of the brain and spinal cord throughout the body, facilitating movement, sensory perception, and organ regulation.
It consists of two main divisions of limbic system: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the Vagus Nerve?
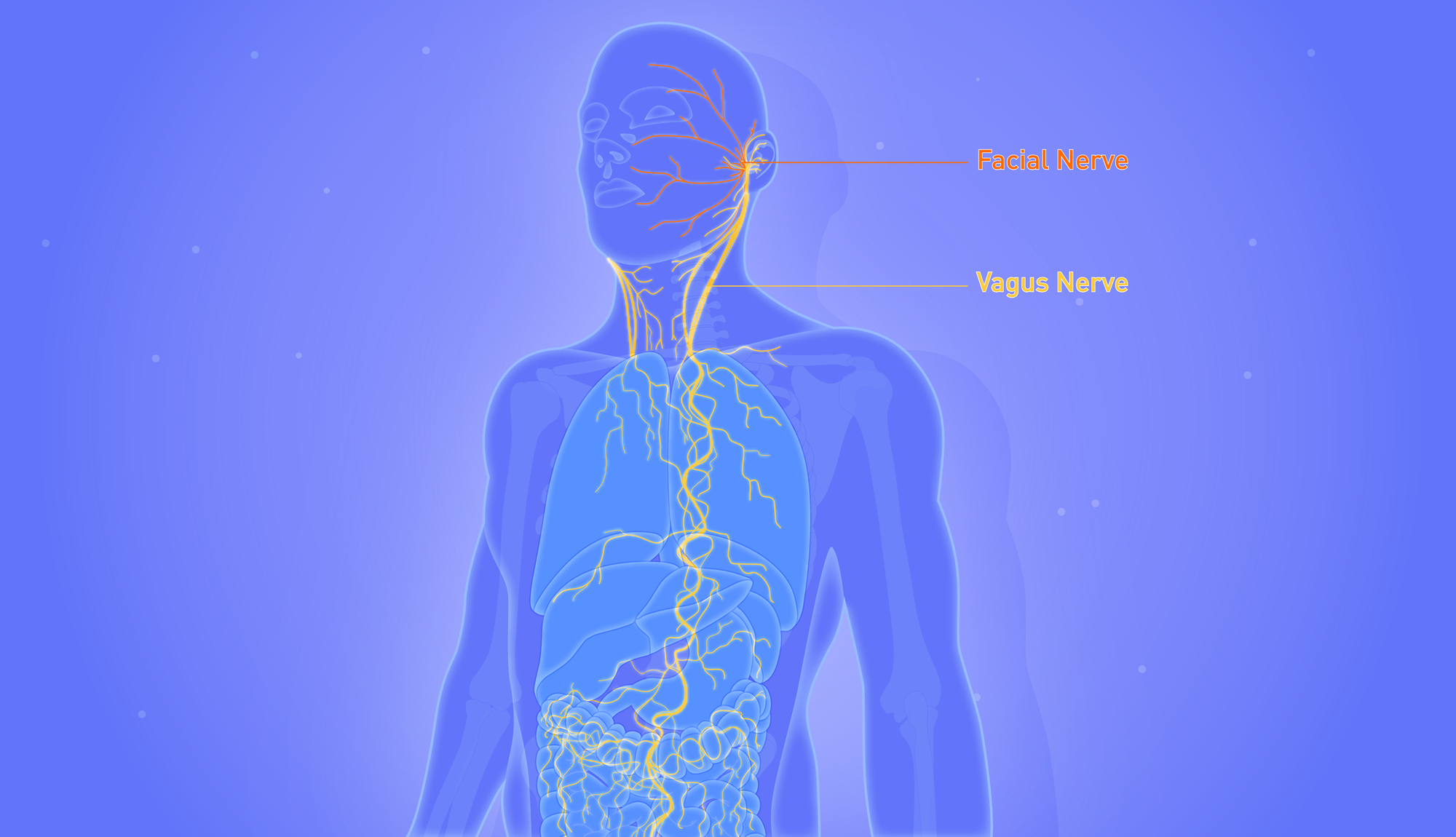
The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body, is a vital component of the parasympathetic nervous system. Often referred to as the "wandering nerve," it innervates numerous organs, including the heart, lungs, digestive, regulated nervous system itself, and glands.
The vagus nerve regulates various bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, inflammation response, and relaxation. It plays a significant role in maintaining overall nervous system health.
What is Nervous System Dysregulation?
Nervous system dysregulation refers to an imbalance or disruption in the functioning of the nervous system. It can manifest as an overactive sympathetic nervous system, responsible for the body's stress response, or an underactive parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for rest and digestion.
Dysregulation can result from chronic stress, trauma, poor lifestyle habits, or genetic factors. When the nervous system is dysregulated, it can lead to a range of physical and mental health problems.
Causes of Nervous System Dysregulation

Nervous system dysregulation can stem from various factors. Chronic stress and anxiety are common contributors, as they can lead to an overactive sympathetic nervous system and disrupt the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Traumatic experiences and stressful events can also impact the nervous system, leaving it in a dysregulated state. Other factors, such as lack of sleep, poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, and exposure to environmental toxins, can also contribute to nervous system dysregulation.
Here are the common causes:
Chronic Stress
Prolonged exposure to stress triggers an overactive sympathetic and autonomic nervous system, which can lead to dysregulation. The constant activation of the body's stress response disrupts the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, affecting overall nervous system function.
Trauma
Physical or emotional trauma, such traumatic events such as accidents, abuse, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), can have a profound impact on the nervous system. Traumatic experiences can leave the nervous system in a heightened state of arousal, leading to dysregulation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits:
Poor nutrition, lack of exercise, inadequate sleep, and excessive alcohol or drug use can all contribute to nervous system dysregulation. These lifestyle factors can negatively impact neurotransmitter function, hormone balance, and overall nervous system health.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins, pollutants, and chemicals can disrupt nervous system function. Heavy metals, pesticides, and certain industrial chemicals can interfere with neurotransmitter signaling and impair the overall balance of the nervous system.
Genetic Factors
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to nervous system dysregulation. Certain genetic variations can affect the functioning of neurotransmitters, receptors, or enzymes involved in nervous system regulation, increasing the likelihood of chronic nervous system dysregulation itself.
Chronic Illness or Inflammation
Chronic health conditions, autoimmune diseases, and systemic inflammation can impact nervous system function. The body's immune response and inflammatory processes can affect neurotransmitter levels, leading to dysregulation.
Medications and Substances
Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and stimulants, can influence the balance of the nervous system. Additionally, substance abuse, including drugs and alcohol, can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of neurotransmitters and contribute to nervous system dysregulation.
It is important to note that these causes can vary from person to person, and an individual may experience nervous system dysregulation due to a combination of factors. Consulting with a healthcare professional or specialist can help identify the underlying causes and develop a personalized plan for addressing and managing nervous system dysregulation.
Common Signs of a Dysregulated Nervous System

A dysregulated nervous system can manifest in several ways. Mood swings and irritability are common, as the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems affects emotional regulation.
Fatigue and insomnia may arise due to sleep disturbances due to imbalances in the sleep-wake cycle. Digestive issues, such as bloating, constipation, or diarrhea, can occur as the dysregulated nervous system affects gut motility and function.
Brain fog and difficulty concentrating are also common, as the disrupted nervous system can impair cognitive function. Increased sensitivity to chronic pain, and inflammation, as well as symptoms of anxiety and depression, are frequently observed in individuals with nervous system dysregulation.
The Link between the Nervous System and Gut Health
The connection between the nervous system and gut health is known as the gut-brain axis. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in this bidirectional communication, transmitting signals between the brain and the digestive system.
A dysregulated nervous system can disrupt this connection, leading to digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gut inflammation, and imbalanced gut microbiota.
Similarly, an unhealthy gut can send signals to the brain, contributing to mood disorders, brain fog, depressive and anxiety disorders.
Therefore, maintaining a healthy nervous system is essential for optimal gut health and overall well-being.
How a Dysregulated Nervous System Negatively Affects Digestion
A dysregulated nervous system can have a significant impact on the digestive process. When the sympathetic nervous system is dominant, as seen during times of stress or anxiety, it inhibits digestion by diverting blood flow away from the digestive organs.
This can result in poor nutrient absorption, slower bowel movements, and an imbalanced gut microbiome.
Additionally, the disruption of the gut-brain axis can lead to increased gut permeability, allowing toxins and undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and further compromising digestive function.
Consequently, individuals may experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
Discovering Nervous System Regulation for Yourself
Healing a dysregulated nervous system requires implementing practices that promote relaxation, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
Mindfulness meditation is a powerful technique that can help regulate the nervous system by activating the parasympathetic response and reducing the dominance of the sympathetic response.
Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can also induce a state of relaxation and stimulate the vagus nerve, promoting a balanced nervous system.
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as yoga or moderate-intensity exercise, has been shown to reduce stress, increase endorphin production, and improve overall nervous system health.
Prioritizing sleep hygiene, ensuring adequate restorative sleep, is essential for nervous system recovery and regulation. Additionally, incorporating stress management techniques like yoga, tai chi, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation can further support nervous system balance.
Techniques to Improve Gut Health and Support a Healthy Nervous System

Stress reduction techniques:
Chronic stress is a significant contributor to nervous system dysregulation. Engaging in stress reduction techniques is crucial for restoring balance. Activities such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises promote relaxation, down blood pressure, reduce stress hormone levels, and activate the parasympathetic nervous system.
These practices help reset stress hormones and regulate the nervous system, improving both gut health and overall well-being.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and prioritizing quality sleep are essential for nervous system recovery. Creating a calming bedtime routine, optimizing sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed can support restorative sleep and regulate your nervous system in balance.
Dietary modifications:
Making dietary changes can positively impact both gut health and the nervous system. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, provides essential nutrients for nervous system function.
Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir supports a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn influences nervous system health. Limiting processed foods, refined sugars, and artificial additives can help reduce inflammation and support optimal gut-brain axis communication.
Supplements that can help:
-
L-theanine: L-theanine is an amino acid known for its calming effects on the nervous system. It promotes relaxation, reduces anxiety, and helps regulate sleep patterns, contributing to a healthier nervous system.
-
Electrolytes: Adequate electrolyte balance is crucial for optimal nerve function. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, support nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and hydration, aiding in nervous system regulation.
-
Magnesium: Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in calming the nervous system and promoting relaxation. It helps regulate neurotransmitter activity and muscle function, aiding in nervous system regulation and supporting healthy digestion.
-
Lions Mane: Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Stimulation: Lion's Mane contains bioactive compounds, including erinacines and hericenones, that have been found to stimulate the production of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF). NGF is a protein that plays a crucial role in the growth, maintenance, and survival of nerve cells. By promoting NGF synthesis, Lion's Mane may support nerve cell health and potentially aid in nerve regeneration and repair.
-
B Vitamins: B vitamins, including B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for nerve health and energy production. They support the synthesis and function of neurotransmitters, promoting a healthy nervous system and optimal digestion.
-
Ginseng: Ginseng exhibits potential neuroprotective properties, meaning it may help protect nerve cells from damage or degeneration. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, potentially supporting overall nervous system health.
-
Omega fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties and support brain health. They can help reduce inflammation in the gut, contributing to improved gut-brain communication and overall nervous system health.
-
Cordyceps: Some studies have suggested that cordyceps may have neuroprotective effects. It may help protect against nerve cell damage and promote nerve cell survival. Cordyceps' neuroprotective properties are thought to be attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Cordyceps has also been found to stimulate nerve cell growth and regeneration in certain studies. It may promote the production of nerve growth factors (NGFs) that play a crucial role in the growth, maintenance, and repair of nerve cells. By supporting nerve cell regeneration, cordyceps may aid in the recovery from nerve injuries or damage.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and healing a dysregulated nervous system is vital for maintaining optimal mental and physical health and well-being. By recognizing the causes and signs of nervous system dysregulation, individuals can take proactive steps to reset and regulate their nervous system.
Incorporating techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, regular physical activity, and stress management practices can promote relaxation and balance in the nervous system.
Additionally, incorporating supplements such as L-theanine, electrolytes, cordyceps, lion's mane, magnesium, B vitamins, and omega fatty acids can support nervous system health and improve gut function.
Gathering the various ingredients up individually and getting the dosing right can be a challenge, thats why we created our gummy Mojo. Our team reverse-engineered a proprietary blend of functional mushrooms, herbs, adaptogens and roots that boost mood, energy and overall well being.
Backed by numerous studies, they taste great, are vegan, gluten-free, and contain no artificial flavors or colors.
Mojo recently won the product of the year at the Microdose awards, and have been featured in Vice, Cool Hunting, Business Insider and Forbes.
Over 1 million gummies sold in the U.S since our launch in 2021 - we're proud to help our community think more clearly, be more productive and feel more connected.
If you want to try Mojo, you can use the following code for 15% off: WELCOME15
By prioritizing self-care and adopting these practices, individuals can nurture a healthy nervous system, leading to improved digestion, reduced stress levels, and enhanced overall well-being.
It is important to note that while these techniques and supplements can be beneficial, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.
They can provide personalized guidance and ensure that these interventions are suitable for your individual needs and health conditions.
Table of contents











